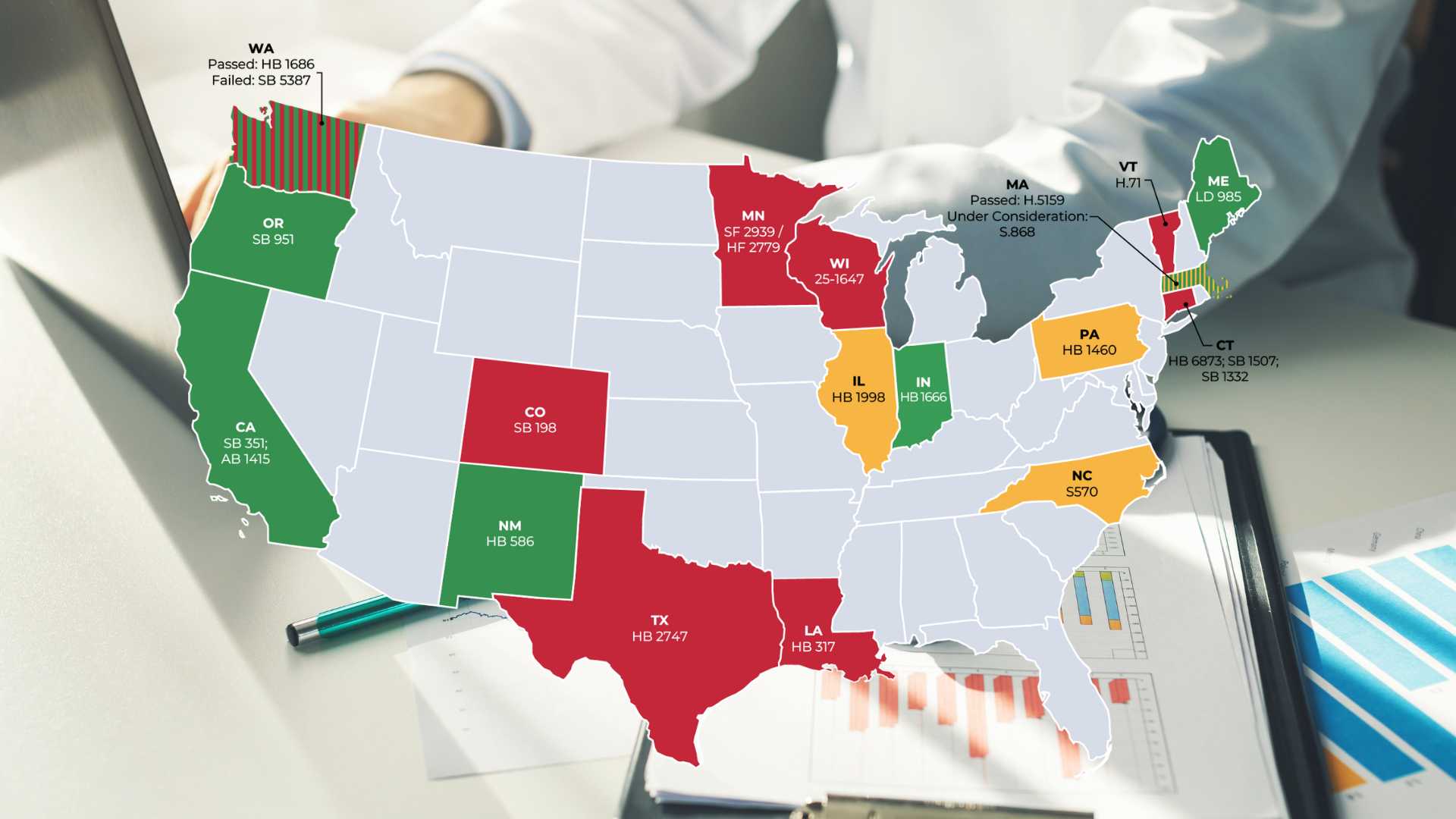
Private equity has invested over $1 trillion in the US healthcare sector over the last decade, and touches virtually every corner of the industry – including hospitals, outpatient providers, clinical research, durable medical equipment, home health and hospice, prison healthcare, and more.
This is despite the fact that private equity investment in healthcare companies carries substantial risk to patients, workers, and investors. The typical private equity investment playbook—pursuing outsized returns over short time horizons while using high levels of debt—may lead to behavior that jeopardizes patient care and increases bankruptcy risk.
For example, many private equity-owned healthcare companies have seen the following issues:
- Reduced staffing, or filling beds without adequate staffing ratios
- Over-reliance on unlicensed staff to reduce labor costs
- Failure to provide adequate training
- Pressure on providers to provide unnecessary and potentially costly services
- Violation of regulations required for participants in Medicare and Medicaid such as anti-kickback provisions, creating litigation risk
Sometimes, private equity financial strategies can even result in layoffs, closures of healthcare facilities, and bankruptcies of entire healthcare systems.
Putting profits before patients is not unique to private equity–owned healthcare companies. But because there’s less transparency around private equity deals and the companies they own, and because private equity firms tend to use more debt than other types of investors to fund their business strategies, the private equity business model can amplify the profit-seeking behaviors that put patients and healthcare workers at risk.

Find all PESP reports on the impacts of private equity investment in key healthcare sectors, including hospitals, behavioral health, and nursing homes.

Find other important private equity research PESP has produced for the healthcare industry, including an archive of all past work.